2023 has been a tough year for stock pickers. The gap between equity factor styles has been vast over H1. Growth, riskier in nature, posted the best performance up 24% year-to-date (YTD) followed closely behind by quality up 20% YTD1. The excitement around artificial intelligence (AI) reached a fever pitch in H1 2023, supporting growth-oriented technology stocks.
As we enter H2 2023, we remain constructive on select areas of global equity markets. The resilience of the US economy has defied all odds. The strength of the US consumer (accounting for 70% of GDP), alongside the fiscal impulse, has been the cornerstone of the US’ extraordinary resilience. While inflation has shown encouraging signs of decline in the US, strong economic momentum alongside a rebound in commodities raises the risk of a re-acceleration of inflation. In turn, rates could remain higher for longer, resulting in Federal Reserve (Fed) rate cuts being delayed until Q1 2024. In such an environment, an enhanced equity income approach could fit well. Even if the earnings outlook weakens in China, proactive policy support via rate cuts could support its stock multiples.
In Europe, where we are likely to witness a mild recession, we believe adopting a more cautious and defensive approach is warranted. Earnings revision ratios remain the strongest in Japan while they are the weakest in emerging markets.
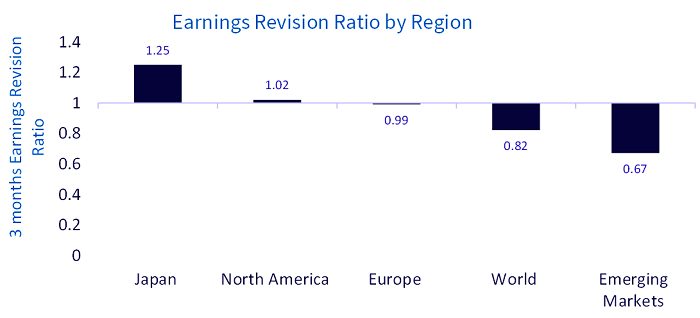
Source: BofA, iQDatabase, WisdomTree, as of 9 October 2023. Historical performance is not an indication of future performance and any investments may go down in value.
US equities are the belle of the ball
It was the narrowest market in history, with just 25% of stocks outperforming the S&P 500. Expectations of cooling inflation aiding the Fed to end its current tightening cycle supported the performance of higher-duration growth stocks. For investors calling for a soft landing, rates are likely to remain at current levels or higher for a longer duration of time. A tight US labour market, with unemployment at historic lows and rising wages, is likely to slow the downward pricing momentum in the service sector. As the market regime transitions, it should provide a ripe opportunity for market breadth2 to improve. Markets may begin to favour value and dividend-paying stocks. History has shown us that breadth tends to improve as the economy recovers from a downturn.
Peak pessimism towards China
China’s reopening rebound has faded. The transition to a less debt-fuelled, less property-reliant and more consumer-driven economy is an important adjustment. We expect government stimulus policies to be aimed at enhancing the efficiency of the private sector. Further iterations of policy rate cuts by the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) are likely to follow; however, outright quantitative easing won’t be on the cards, as it is likely to further weaken the yuan, which the PBOC would like to avoid. With a low correlation to US equities (at 20x P/E)3 coupled with a high valuation discount, pockets of China continue to provide good investment prospects.
Pockets of opportunity in non-state-owned enterprises
Non-state-owned enterprises, particularly within the Technology, Communication Services and Health Care sectors, faced the brunt of China’s regulatory crackdown. These regulatory interventions stifled growth in key sectors such as e-commerce, mobile payment, ride-hailing, and online education. It also resulted in the suspension of initial public offerings (IPOs) and delisting of Chinese internet companies. Growing political frictions in supply chains are incentivising China to regain independence in the semiconductor and hardware space. Chinese technology companies are trading at a significant discount compared to US peers, offering plenty of room to catch up.
Prefer defensives over cyclicals as Europe runs out of steam
Nearly six months back, investors marvelled at how the euro-area economy had emerged from the energy crisis. That momentum appears to be fading as China’s recovery slows down, consumer confidence declines, and the impact of tighter monetary policy gains a stronghold on the economy. Higher inflation over the past year is holding back demand from households, which is hurting growth.
The monetary tightening over the past year not only triggered an increase in real rates, it also impacted borrowers’ credit metrics. Owing to this, eurozone banks have tightened their lending standards.4 Banks remain the primary source of corporate funding in Europe. The credit impulse—that is, the annual change in the growth of credit relative to GDP—in the euro area reached its lowest point since 2010.
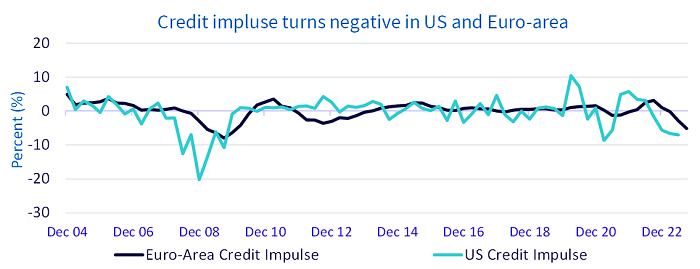
Source: Bloomberg, WisdomTree, as of 29 September 2023. Historical performance is not an indication of future performance and any investments may go down in value.
TINA is alive in Japan
There is no alternative (TINA) to equities is still alive in Japan. This is evident from higher equity risk premiums of 2.97% for Japan compared to 0.41% in the US.5 While the rest of the world has been busy trying to quell the inflation fires, Japan has emerged from the COVID-19 lockdowns with a faster pace of growth and higher inflation. A combination of higher equity risk premiums, a weaker yen supportive of the Japanese export market, corporate reforms, and attractive valuations have been important catalysts for equities.
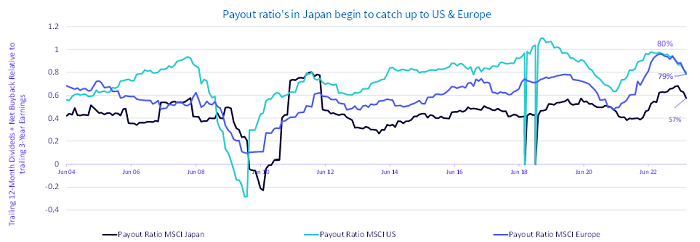
Source: FactSet, WisdomTree, as of 29 September 2023. Historical performance is not an indication of future performance and any investments may go down in value.
Policy shift still remains loose
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) took a significant step towards normalisation in July by announcing a further adjustment to its yield curve control (YCC) regime. The BOJ formally changing its course constitutes an acknowledgement that inflation is returning to the Japanese economy. Yet the BOJ lowered its (median) inflation forecast for fiscal year (FY) 2024 to +1.9% and left its FY 2025 projection unchanged at +1.6%, in effect justifying ongoing easing by the BOJ. With Japan’s nominal growth rising over the coming years, the revised policy by the BOJ still remains loose, supporting the case for Japanese equities. Historically, a weaker yen has benefitted the performance of Japanese exporters as it enhances their competitive advantage. Adopting a tilt towards dividend-paying Japanese equities is likely to reap the benefits of not only a weaker yen but also corporate governance reforms.
Conclusion
As we progress into year-end, the outlook remains more nuanced. In the US, we favour value and dividend stocks as equity market breadth improves. While China’s problems in the housing sector are likely to remain a drag on domestic demand, we do see pockets of opportunity in undervalued sectors – technology and healthcare. Given the strong manufacturing headwinds facing Europe, we expect weak growth in the eurozone for the remainder of 2023, potentially favouring a tilt towards defensive stocks.
Sources
1 Bloomberg as of 11 October 2023.
2 Breadth is measured by comparing the equal weighted performance versus the market cap-weighted performance of the US stocks listed on the S&P 500 Index.
3 P/E = price to earnings ratio.
4 Euro area Bank Lending Survey (BLS), April 2023.
5 Bloomberg, WisdomTree, as of 29 September 2023. Equity risk premium is the difference between the earnings yield and the respective 10-Year Government Bond Yield.

