The challenge for central banks has grown more complicated with volatility in bond markets and mounting inflationary pressures. Investors face a similar balancing act in navigating the central bank policy divergence that is set to characterise 2022 and beyond.
Key takeaways
- Higher interest rate expectations coupled with wider credit spreads are a challenge for central banks to manage.
- Some economies will be required to tighten policy quicker than others, partly because of regional differences in sensitivity to the commodity price shock.
- Divergence in policy could potentially create compelling opportunities for investors, but this will require careful navigation, such as assessing what is priced into interest rate expectations and the potential path ahead.
A tougher challenge for central banks
The simultaneous move higher in interest rate expectations due to persistent high inflation and the widening of credit spreads exacerbates the complicated task for central banks in navigating a soft landing for their economies. From a regional perspective, there is some limit to the degree in which monetary policy can diverge without weakening the exchange rates of the laggards (which are further behind in their hiking cycles) and compounding domestic inflation through higher import costs. Except for China, we may likely see a tightening from all major central banks, but this misses the bigger picture that certain regions and economies might be required to tighten policy faster than others. This is because the starting point of initial economic conditions from their pandemic recovery is different, as is their relative sensitivity to the commodity shock now in train.
In particular, many countries in Europe will not enjoy any economic uplift from higher commodity prices, as they suffer from the combined forces of risk aversion, a rising energy import bill, and a real income squeeze. European growth looks set to be hit much harder by the war, not only due to its regional proximity to the conflict but also due to its energy dependence on Russia. On the other hand, the US economy looks relatively more insulated as a producer of both oil and gas domestically, and Fed chair Powell has also signalled that he doesn’t see a major impact from the Russia conflict on the hiking cycle in the US in his recent communications. This is reflected in the table below which shows research from Goldman Sachs that the US and China could be similarly affected by the oil and gas price shock, while the Euro Area could fare the worst.
2022 GDP impact of oil and gas shock (%)
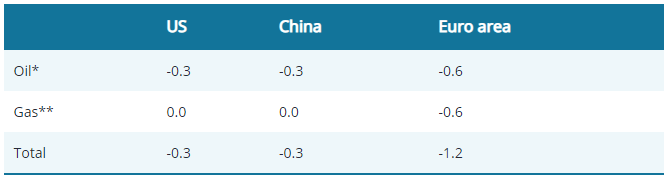
Source: Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research (GIR), as at 6 March 2022. Past performance does not predict future returns. **The figures above assume best-case scenario (existing disruptions scenario), but GIR’s base case assumes flow disruptions to Russia’s gas exports through Ukraine.
Aside from the differing impacts of the recent energy price surge on the likes of Europe and the US, we see other noteworthy examples of divergence that potentially offers investors compelling opportunities. In the developed economies, Switzerland offers an interesting case study on the differing priorities of certain central banks. The Swiss national bank (SNB) is extremely sensitive to the strength of the swiss franc and has a history of intervening directly and using policy rates to ameliorate offshore demand for its currency.
With the energy price move and uncertainty arising from the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the swiss franc has benefitted from investor flight to safe havens, which in turn has prompted concerned comments from the central bank. As Switzerland is less exposed to the inflationary forces affecting many other countries, we believe that tighter policy from the SNB is exceptionally unlikely with a possibility that we could yet see even more negative rates. Switzerland already has the world’s lowest interest rates at -0.75%1. This is one of the options on the table for the SNB, as the country’s banking system is properly equipped to deal with such negative interest rates. Alternatively, the SNB continues to reassure markets that it may still intervene in forex markets or it could set a minimum exchange rate versus the euro, as we discussed in a recent article.
How can investors navigate this environment?
Navigating this environment requires a careful balance between generating income from the higher credit spreads on offer and using government bond duration – or interest rate sensitivity – as a counterbalance. While we are in a rising rate environment, it is important to consider just how much has been priced into government yield curves (which indicate market expectations for rates) – short-term rates significantly up, but terminal rates very low.
The US 2s5s yield curve is close to inverting
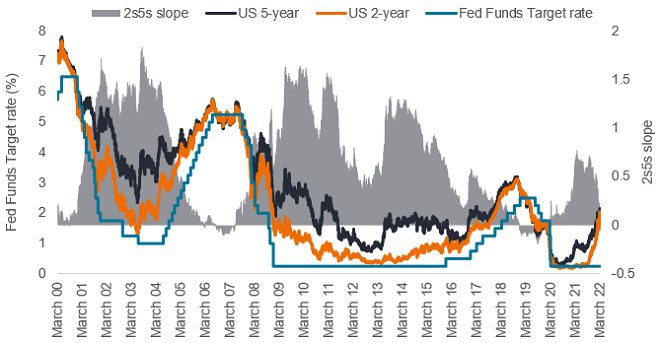
Central bankers seem to be fixated on the worry that the combination of a tight labour market and high inflation could lead to a de-anchoring of inflation expectations. This would warrant rate hikes being front loaded. However, we continue to hold our view that while rate hikes are coming, the inversion of yield curves – such as the 2s5s which is the difference in basis points between the 5-year and 2-year Treasury yield – that has already occurred or taken place in markets such as the US and UK is anomalous, given that this phenomenon should occur towards the end of the hiking cycle not at the start. Yield curves have flattened significantly even before rate hikes have even begun.
It can be argued that inverted yield curves may make some intuitive sense given current elevated inflation levels, but we believe that the path of rates indicated by market pricing is highly unlikely to be delivered. In addition, the curve shape suggests that this rate hiking cycle is likely to be shorter than many anticipate as well as sharper than we have experienced in recent periods.
A multi-speed recovery continues
More broadly, most of the world’s economies are subject to decent growth and elevated inflation as the recovery from the pandemic continues at varying speeds. Going forward, we see a general plurality of central banks considering some formulation of tighter policy. China, however, is moving in the opposite direction. A combination of far stricter COVID restrictions, a vaccine (Sinovac) that appears less effective in preventing the virus than the MRNA vaccines used elsewhere and an economic policy focused on restraining the property sector over leverage concerns and general fiscal prudence has resulted in much slower growth than seen historically. In China, monetary policy appears to be leaning more towards accommodation than tightening. The degree to which the Chinese economy may be out of sync with much of the rest of the global economy is highly noteworthy and offers both investment opportunity as well as an insight into how the ‘multi-polar’ world may operate going forward.
Footnotes
1 Source: Trading economics, 10 March 2022.
Glossary
Credit spread: The difference in the yield of corporate bonds over equivalent government bonds.
Consumer price index (CPI): A measure that examines the price change of a basket of consumer goods and services over time. It is used to estimate ‘inflation’.
Duration: How far a fixed income security or portfolio is sensitive to a change in interest rates, measured in terms of the weighted average of all the security/portfolio’s remaining cash flows (both coupons and principal). It is expressed as a number of years.
Fiscal: Connected with government taxes, debts and spending.
Inflation: The rate at which the prices of goods and services are rising in an economy.
Leverage: The use of borrowing to increase exposure to an asset/market. This can be done by borrowing cash and using it to buy an asset, or by using financial instruments such as derivatives to simulate the effect of borrowing for further investment in assets.
Monetary policy: Central bank policies aimed at influencing the level of inflationand growth in an economy. It includes controlling interest rates and the supply of money. Monetary stimulus refers to a central bank increasing the supply of money and lowering borrowing costs. Monetary tightening refers to central bank activity aimed at curbing inflation and slowing down growth in the economy by raising interest rates and reducing the supply of money.
Terminal rate: Also called the natural or neutral interest rate. It is the rate that is consistent with full employment and capacity utilisation and stable prices.
Yield curve: A graph that plots the yields of similar quality bonds against their maturities. In a normal/upward sloping yield curve, longer maturity bond yields are higher than short-term bond yields. A yield curve can signal market expectations about a country’s economic direction.
Yield: The level of income on a security, typically expressed as a percentage rate.
Volatility: The rate and extent at which the price of a portfolio, security or index, moves up and down. If the price swings up and down with large movements, it has high volatility. If the price moves more slowly and to a lesser extent, it has lower volatility. It is used as a measure of the riskiness of an investment.
These are the views of the author at the time of publication and may differ from the views of other individuals/teams at Janus Henderson Investors. Any securities, funds, sectors and indices mentioned within this article do not constitute or form part of any offer or solicitation to buy or sell them.
Past performance does not predict future returns. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.

