Most investors already allocate to emerging market debt (EMD). It is an area of investment that has become an established part of many fixed-income portfolios. EMD now represents 18.0% of global bond issuance, which is significant.¹
However, most investors also still hold far less than this amount as a fixed income allocation. In the past, smaller allocations may have been warranted. Back then there was less liquidity, greater default risk and less diversity to be found in EMD.
This picture has now changed. EMD as a market has matured. For instance, many sovereign bonds issued in emerging markets have gradually been rated upwards, moving from high yield to investment-grade status. By contrast, many developed market issuers have experienced moderate downgrades since the financial crisis 13 years ago. Subsequently, there has been a convergence in credit quality between the two.
Emerging market bonds have become an established group of asset classes
EMD is no longer a niche allocation. It has swelled to over USD 4.6 tn in assets in just two decades (see Chart 1). It should also not be defined as a single asset class, but rather as a series of different asset classes that offer unique sources of risk premia (see Chart 2).
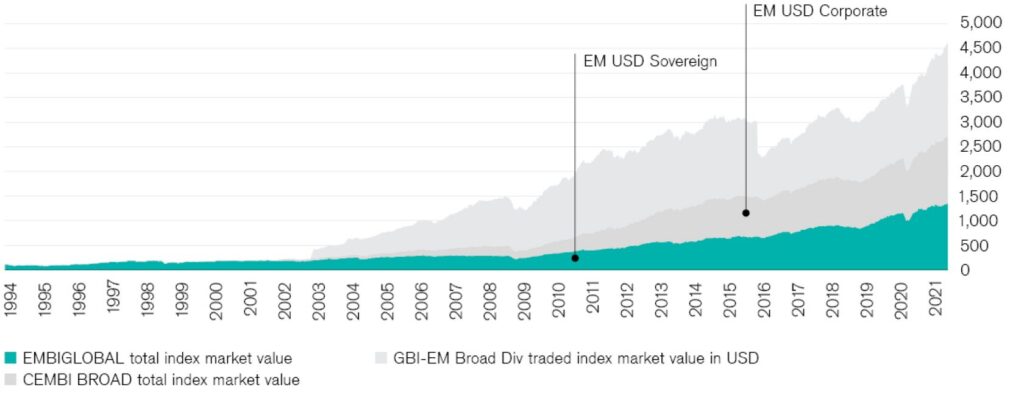
The emerging market debt universe has swelled to USD 4.6 trillion
Source J.P. Morgan indices, as of May 31, 2021
There’s a huge variety of emerging market bonds available
There are hard-currency emerging market bonds. These include sovereign bonds (issued by governments) and corporate bonds (issued by companies). Both are asset classes in their own right.
These hard-currency bonds are typically denominated either in US dollars or other major currencies, such as euros, pound sterling or Japanese yen. The hard-currency market alone accounts for USD 3 tn in assets. To put this into context, this is half the size of the US investment-grade corporate bond market, and more than twice the size of the US high-yield market.2

Source J.P. Morgan indices, Credit Suisse (May 2021)
*CEMBI – Corporate Emerging Markets Bond Index, EMBIG – Emerging Market Bond Index Global
Added to hard-currency bonds, there are also local-currency emerging market bonds. This market has grown rapidly over the past decade. Burgeoning US government deficits and the potential for a future weakening of the US dollar has encouraged greater levels of local currency bond issuance from emerging markets. From an investor’s perspective this offers even more ways to diversify a fixed income portfolio and provide additional sources of risk premium.
Overall, this has become a huge and diverse market that is difficult to ignore.
Investors should combine both a passive and active approach with EMD
There are benefits from combining both a passive and active approach to emerging market debt. In combination, both can offer a very effective way to manage an emerging market debt portfolio.
Passive investing
There are now significant amounts of liquidity offered across the emerging market bond universe as the market has matured. There have also been significant technological developments in bond indexation, which have helped investors gain quick access to this market while minimizing tracking error risk.
This gives investors an enormous amount of flexibility in managing their overall exposure to emerging market bonds, regardless of which asset class they focus on. It is relatively easy to quickly add or remove exposure to an index and there are a wide variety of indices on offer. Two of the most popular are the JPM EMBI Global Diversified index, which comprises USD-denominated debt, and the JPM GBI-EM Global Diversified index, which contains local currency debt.
Active investing
Beyond passive investing, there are also a variety of risk premia on offer if you take an active approach. For instance, there are inefficiencies found across EMD due to the size and complexity of this market. This is an area where active portfolio management can add value.
Emerging markets differ in how they issue and structure debt. An experienced active investor understands these different micro-structures within each market and can take advantage of these differences.
They can also gain exposure to bonds that lie outside the index and actively position themselves relative to an index to manage exposure to interest rate risk or credit risk. Overall, the broader universe that an active manager has access to can help them improve liquidity, the level of yield and exposure to duration risk.
They can also take advantage of special situations. For instance, they could tactically tilt into distressed bonds that are shunned by risk-averse investors. They can also capitalize on inefficiencies within the market by either selling emerging market bonds in anticipation of a downgrade or buying at lower prices following a downgrade.
Another interesting source of return is through the primary issuance market. Unlike an index, active managers can actively participate during issuance season. They can also take advantage of smaller issuers that an index might not capture due to liquidity constraints within the index.
There are benefits from taking both a passive and active approach to emerging market bonds. By combining the two, an investor can build a dynamic and well diversified emerging market debt portfolio.
2 J.P. Morgan
This material has been prepared by Credit Suisse Group AG and/or its affiliates (“Credit Suisse”).
It is provided for informational and illustrative purposes only, does not constitute an advertisement, appraisal, investment research, research recommendations, investment recommendations or information recommending or suggesting an investment strategy, and it does not contain financial analysis. Moreover it does not constitute an invitation or an offer to the public or on a private basis to subscribe for or purchase products or services. Benchmarks, to the extent mentioned, are used solely for purposes of comparison. The information contained in this document has been provided as a general commentary only and does not constitute any form of personal recommendation, investment advice, legal, tax, accounting or other advice or recommendation or any other financial service. It does not take into account the investment objectives, financial situation or needs, or knowledge and experience of any persons. The information provided is not intended to constitute any kind of basis on which to make an investment, divestment or retention decision. Credit Suisse recommends that any person potentially interested in the elements described in this document shall seek to obtain relevant information and advice (including but not limited to risks) prior to taking any investment decision.
The information contained herein was provided as at the date of writing, and may no longer be up to date on the date on which the reader may receive or access the information. It may change at any time without notice and with no obligation to update.
To the extent that this material contains statements about future performance, such statements are forward looking and subject to a number of risks and uncertainties. It should be noted that historical returns, past performance and financial market scenarios are no reliable indicator of future performance. Significant losses are always possible.
This material is not directed to, or intended for distribution to or use by, any person or entity who is a citizen or resident of, or is located in, any jurisdiction where such distribution, publication, availability or use would be contrary to applicable law or regulation, or which would subject Credit Suisse to any registration or licensing requirement within such jurisdiction.
The recipient is informed that a possible business connection may exist between a legal entity referenced in the present document and an entity part of Credit Suisse and that it may not be excluded that potential conflict of interests may result from such connection.
This document has been prepared from sources Credit Suisse believes to be reliable but does not guarantee its accuracy or completeness.
Credit Suisse may be providing, or have provided within the previous 12 months, significant advice or investment services in relation to any company or issuer mentioned.
This document may provide the addresses of, or contain hyperlinks to, websites. Credit Suisse has not reviewed the linked site and takes no responsibility for the content contained therein. Such address or hyperlink (including addresses or hyperlinks to Credit Suisse’s own website material) is provided solely for your convenience and information and the content of the linked site does not in any way form part of this document. Accessing such website or following such link through this document or Credit Suisse’s website shall be at your own risk.
This document is intended only for the person to whom it is issued by Credit Suisse. It may not be reproduced either in whole, or in part, without Credit Suisse’s prior written permission.
Copyright © 2022. CREDIT SUISSE GROUP AG and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.

