The Ethereum blockchain enabled withdrawals of staked ether (ETH) and accrued rewards in April 2023, unlocking the potential for ether holders to earn a passive income through staking. Following this important development, WisdomTree activated staking in its physically-backed ether exchange-traded product (ETP), WisdomTree Physical Ethereum (ETHW) on 21 August 2023. This means that investors can easily access ether and receive staking rewards via ETHW.
Before outlining this in more detail, and highlighting what it means for investors, let’s recap the basics.
What is staking?
Ethereum network validators run software in their computers and are expected to be online 24/7. Each validator must deposit 32 ETH in a smart contract to be able to participate in the verification process. The maximum effective balance is 32 ETH, which means that if a validator has more than 32 ETH in a smart contract, they do not earn more rewards or are not selected more often to propose a block. This also means that compounding rewards is currently not possible. The Ethereum foundation is considering an initiative EIP-7251 (Ethereum improvement proposal) at the moment, and the acceptance of this proposal could increase the maximum effective balance from 32 to 2048 ETH2. The proposal suggests that the minimum amount required to stake ETH would remain at 32 ETH, but the maximum effective balance could increase to 2048 ETH meaning that compounding ETH rewards might be possible.
Where does staking yield come from?
In a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, ‘consensus’ is reached when staking participants validate the blockchain’s transactions. On the Ethereum blockchain, each round of validation takes 6.4 minutes and bundles 32 blocks of transactions. These bundles are called epochs and transactions become irreversible once two more epochs are added to the blockchain. During the transaction validation process, validators are randomly grouped into committees of 128 members and assigned a particular block.
Inside each committee, one member of the group is randomly chosen to propose a new block of transactions and the remaining members vote on the proposal and ‘attest’ that the transactions are valid. Once a majority of the committee has attested the new block, it is added to the blockchain. After this, the proposer receives their base ETH reward (proposer reward), and the attesters receive the remaining portion of the base reward (attester reward). Attesters only receive their full amount of the reward if they respond within 6.4 – 12.8 minutes (which corresponds to 1 epoch and a second chance to attest during the subsequent epoch)3. If a staker/validator acts dishonestly their staked funds can be slashed4. If the validator does not respond for 4 epochs, an ‘inactivity leak’ mechanism is activated to very gradually reduce the balance of the staked ether . In addition, to proposer and attester rewards, a validator may also be chosen to participate in ‘sync committees’, where they can generate sync committee rewards but these fees are relatively infrequent.
In addition to these consensus rewards, a validator can generate rewards from execution-related tasks. These execution rewards include tips/priority fees (not the same as ‘gas’ or transaction fees), which users pay to incentivise validators to include their transaction to the next block, or maximum extractable value (MEV) fees, where the validator uses certain block-building software to rearrange or reorder transactions in a block. MEV block-building can also be outsourced to a third party.
Total number of validators and staked ETH has risen 37% in six months
Following the Shanghai upgrade in April 2023, there was a significant uptick in the number of new validators but since then this number has moderated. However, the total number of validators continues to rise and in late August 2023 there were 750,926 validators6 with over 24 million ETH staked on the network (worth $39.8 billion). This translates to approximately 20% of ETH in circulation (total ETH issuance is approximately 120 million). These numbers are up approximately 44% since February 2023.
Figure 1: Ethereum: ETH 2.0 total number of validators (14 day moving average)
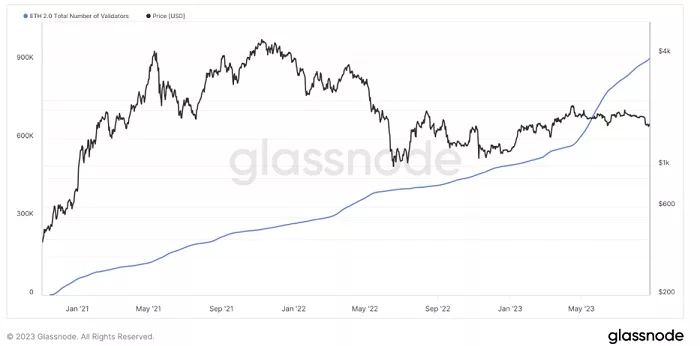
Source: Glassnode, August 2023. Historical performance is not an indication of future performance and any investments may go down in value.
We believe there is significant institutional interest in ETH staking and expect the amount of staked ETH to increase further in the coming months to over 50%. With many other tokens, the staking ratio is between 40-98%, which makes ETH’s staking ratio still relatively low. The more validators there are, the lower the staking yield is per validator but, on the other hand, higher decentralisation and higher staked ratio of ETH makes attacking the blockchain more difficult.
Strong interest in staked ETH continues
The activation queue on Ethereum has been steadily increasing. In late August 2023, there were 58,994 pending validators7 in the activation queue, which translates to approximately 8% of total ETH validators. This means that it could take up to a month to process these activations. The exit queue, however, had less than 100 validators on the exit queue8. There was a spike in exits right after the staked ETH withdrawals were enabled as there was natural churn among staking service providers. Kraken, particularly, exited at that point due to a settlement with the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Figure 2: Ether deposits and withdrawals
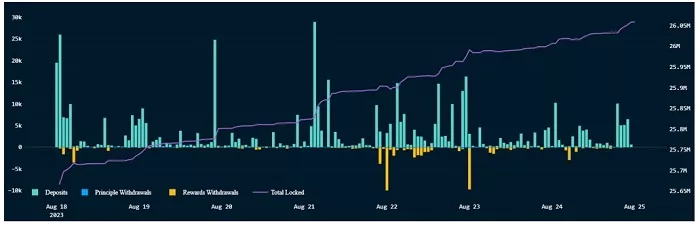
Source: Nansen.ai, August 2023. Historical performance is not an indication of future performance and any investments may go down in value.
No need to handle private keys or wallets with WisdomTree Physical Ethereum
WisdomTree Physical Ethereum is a physically-backed exchange-traded product (ETP) that gives investors exposure to Ethereum without having to deal with managing private keys, wallets or other aspects of self-custody and enabling management of all assets in one place.
Following our commitment and proven track record of innovation and delivering institutional-grade products, WisdomTree has worked closely with its custodian to activate staking in its physically-backed ether ETP, WisdomTree Physical Ethereum on 21 August 2023. It has implemented a transparent and risk-managed approach to staking with 75% of staking rewards passed on to investors via increasing the coin entitlement of the ETP.
WisdomTree Physical Ethereum
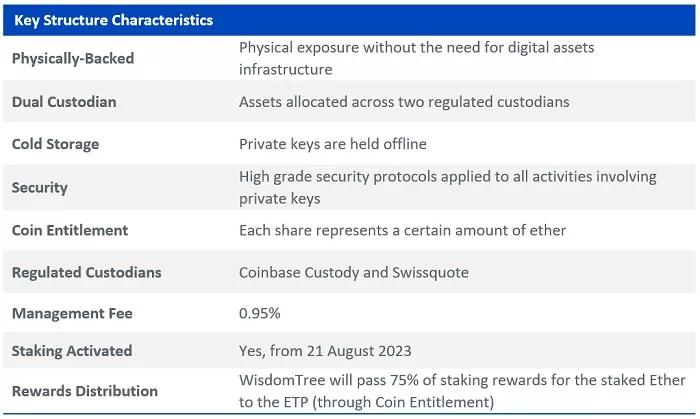
Investing in ether via an ETP allows investors to experience the benefits of traditional financial infrastructure and product structuring and the WisdomTree Physical Ethereum provides investors with a simple, secure and cost-efficient way to gain exposure to the price of ether and receive staking rewards.
Sources
1 Source Ethereum.org.
2 Source Ethereum.org.
3 Source https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/consensus-mechanisms/pos/attestations/
4 Source Slashing: some or all of the staked ETH can be lost. On Ethereum, slashing is automatic for double signing and serious downtime.
5 Source https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/consensus-mechanisms/pos/rewards-and-penalties/
6 Source Beaconcha.in
7 Source Validatorqueue.com
8 Source Validatorqueue.com

